Once The Product Or Service Passes The Business Analysis Test, It Moves Into What Stage?
What is the Production Life Cycle?
The Product Life Cycle (PLC) defines the stages that a product moves through in the market place as it enters, becomes established, and exits the marketplace. In other words, the product life cycle describes the stages that a product is likely to experience. Information technology is a useful tool for managers to help them analyze and develop strategies for their products as they enter and exit each phase.
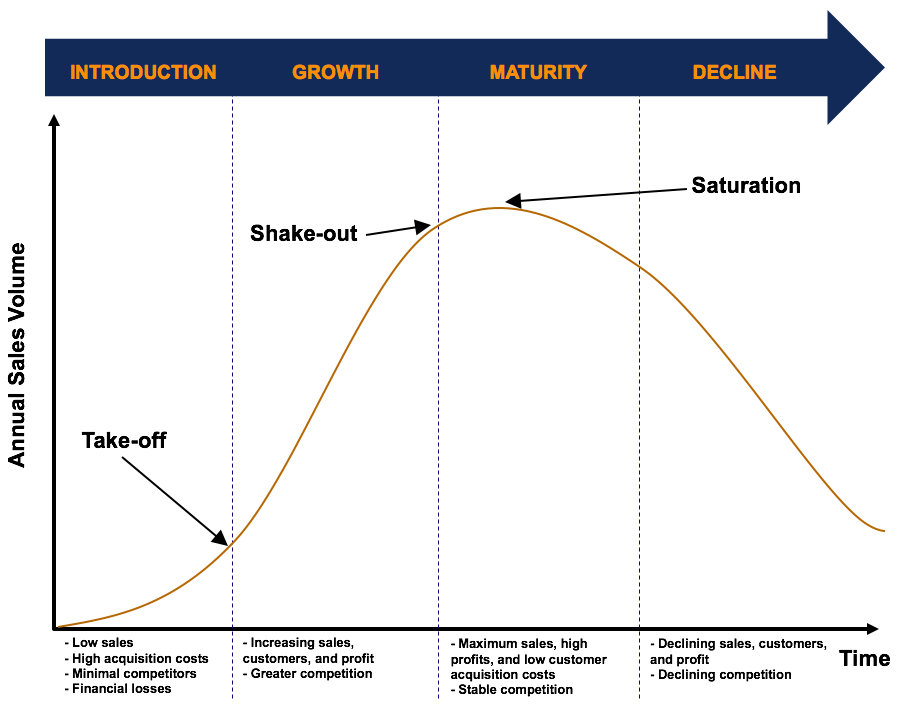
Stages in the Product Life Bike
The four stages in the production life bicycle are:
- Introduction
- Growth
- Maturity
- Decline
ane. Introduction Stage
When a product outset launches, sales will typically be low and grow slowly. In this stage, company profit is small (if any) as the product is new and untested. The introduction phase requires significant marketing efforts, as customers may be unwilling or unlikely to examination the product. At that place are no benefits from economies of calibration, every bit production chapters is non maximized.
The underlying goal in the introduction stage is to gain widespread production recognition and stimulate trials of the product by consumers. Marketing efforts should be focused on the customer base of innovators – those most likely to buy a new product. At that place are 2 cost-setting strategies in the introduction stage:
- Price skimming: Charging an initially high price and gradually reducing ("skimming") the price as the market grows.
- Price penetration: Establishing a low toll to chop-chop enter the market place and capture market share, earlier increasing prices relative to market growth.
2. Growth Phase
If the product continues to thrive and meet marketplace needs, the product will enter the growth phase. In the growth stage, sales revenue normally grows exponentially from the take-off point. Economies of scale are realized as sales revenues increase faster than costs and production reaches capacity.
Contest in the growth phase is often violent, as competitors innovate like products. In the growth stage, the market place grows, competition intensifies, sales rise, and the number of customers increases. Price undercutting in the growth phase tends to exist rare, equally companies in this stage can increase their sales by attracting new customers to their product offerings.
iii. Maturity Stage
Eventually, the market grows to capacity, and sales growth of the product declines. In this phase, price undercutting and increased promotional efforts are mutual as companies try to capture customers from competitors. Due to fierce competition, weaker competitors will eventually leave the marketplace – the milkshake-out. The strongest players in the market remain to saturate and dominate the stable market.
The biggest challenge in the maturity stage is trying to maintain profitability and prevent sales from failing. Retaining customer brand loyalty is key in the maturity stage. In addition, to re-innovate itself, companies typically utilize strategies such as market evolution, product evolution, or marketing innovation to ensure that the product remains successful and stays in the maturity stage.
four. Decline Phase
In the pass up stage, sales of the product start to fall and profitability decreases. This is primarily due to the market entry of other innovative or substitute products that satisfy customer needs meliorate than the current production. There are several strategies that can be employed in the pass up stage, for case:
- Reduce marketing efforts and try to maximize the life of the production for as long as possible (called milking or harvesting).
- Slowly reducing distribution channels and pulling the product from underperforming geographic areas. Such a strategy allows the company to pull the product out and attempt to introduce a replacement product.
- Selling the product to a niche operator or subcontractor. This allows the company to dispose of a low-turn a profit product while retaining loyal customers.
Additional Resources
CFI offers the Financial Modeling & Valuation Analyst (FMVA)™ certification plan for those looking to take their careers to the next level. To proceed learning and advancing your career, the following CFI resources volition be helpful:
- AIDA Model
- Beachhead Strategy
- Buyer Types
- Market Planning
Source: https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/knowledge/other/product-life-cycle/
Posted by: monroebestudy.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Once The Product Or Service Passes The Business Analysis Test, It Moves Into What Stage?"
Post a Comment